Today, there are more than 50 types of Application of ceramic materials in cars industry, and this number is still increasing.
Among the applications of these materials can be the construction of a new and heat-resistant brake system with high hardness, engines without the need for cooling, all kinds of sensors used in car welfare systems, all kinds of glass and side mirrors, body protection surfaces for cars.
Bulletproof, paint coating. It is also possible to refer to car engine spark plugs, exhaust catalyst and electrical insulation used to make the car body paint shiny and scratch resistant in this article. In the following, act group describes each of them in detail.
Introduction
When most people hear the name of ceramic materials, they remember the traditional uses of this precious material, but today, the use of ceramic materials in cars is used as advanced materials with unique electrical, mechanical, optical and magnetic properties.
During recent years, the use of ceramics in the automotive industry is increasing day by day. The special and desirable properties of ceramics have made their use the only solution in many cases.
These materials, which have good tolerance against thermal loads and can withstand temperatures up to 1650 degrees Celsius, require a simpler cooling system or do not need this system at all. Due to its light weight, this material is used in making engines. Because it will reduce the weight of the car.
Due to working at high temperatures, ceramic engines are able to make the fueling process more efficient and reduce the amount of fuel consumed and as a result the pollution caused by it. Also, the use of these engines allows designers to use multiple fuels.
All kinds of sensors and transducers
Are used in making sensors such as water temperature sensor, tire inflation sensor, remaining fuel sensor, park assist systems and some other sensors.
For example, in the fuel level sensor, a piezoceramic transducer is placed at the bottom of the fuel tank, which produces sound waves by applying an electric current.
Then this electric current is cut off and the generated sound waves reflect on the surface of the fuel inside the tank.
When the reflected waves hit the converter, an electric current is created in it, and the computer measures the amount of remaining fuel by measuring the time of the wave’s round trip.
Other types of piezoceramics include piezoceramics used in comfort systems such as chair massagers, which are composed of two ceramic layers separated by a carbon fiber layer.
One of these two ceramic layers is expanded by the application of electric current and causes the entire assembly to bend (similar to what happens in a thermostat due to temperature changes).
In this way, the valve is opened and the air flow creates a massage mode in specific areas inside the seat. The main advantage of using these materials compared to metal materials is 20-30% more flexibility and less weight (Figure 1).
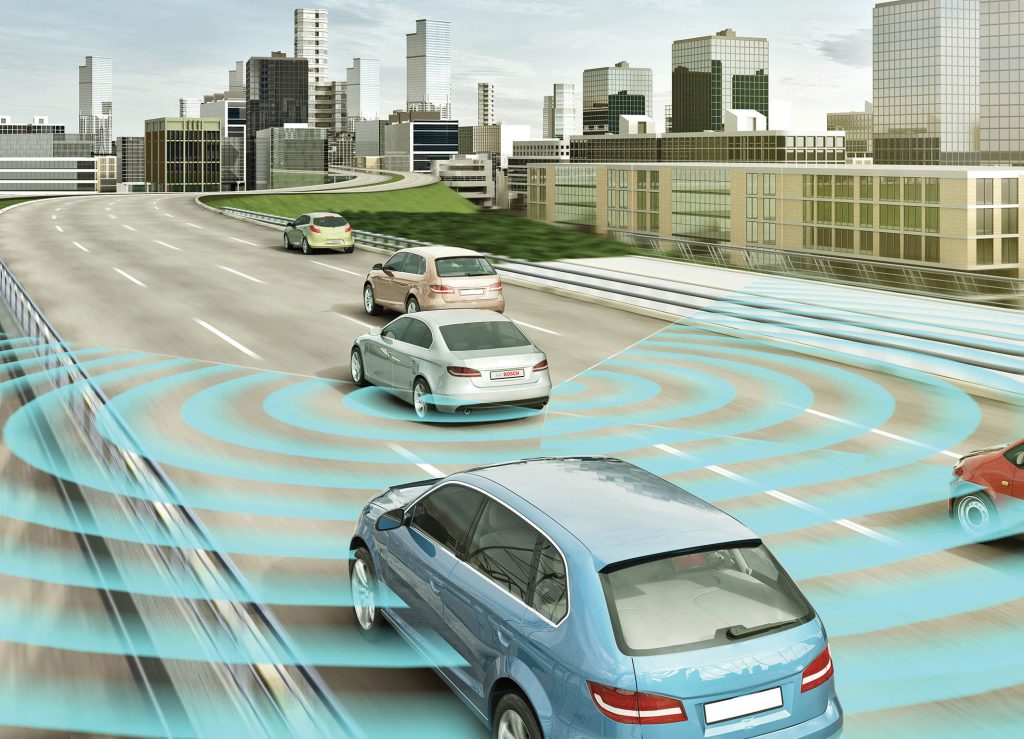

figure 1
Advanced ceramic bearing and washers have high strength and chemical and thermal resistance.
For this reason, they are used in making water pump bearings and injector sealing parts and gaskets.
In diesel engines, after air compression, the temperature reaches more than 800 degrees Celsius, and the injector must be able to inject fuel with a pressure of 2000 bar inside the combustion chamber.
The high hardness and thermal and chemical resistance of ceramics has made it possible to use them in these systems (Figure 2).
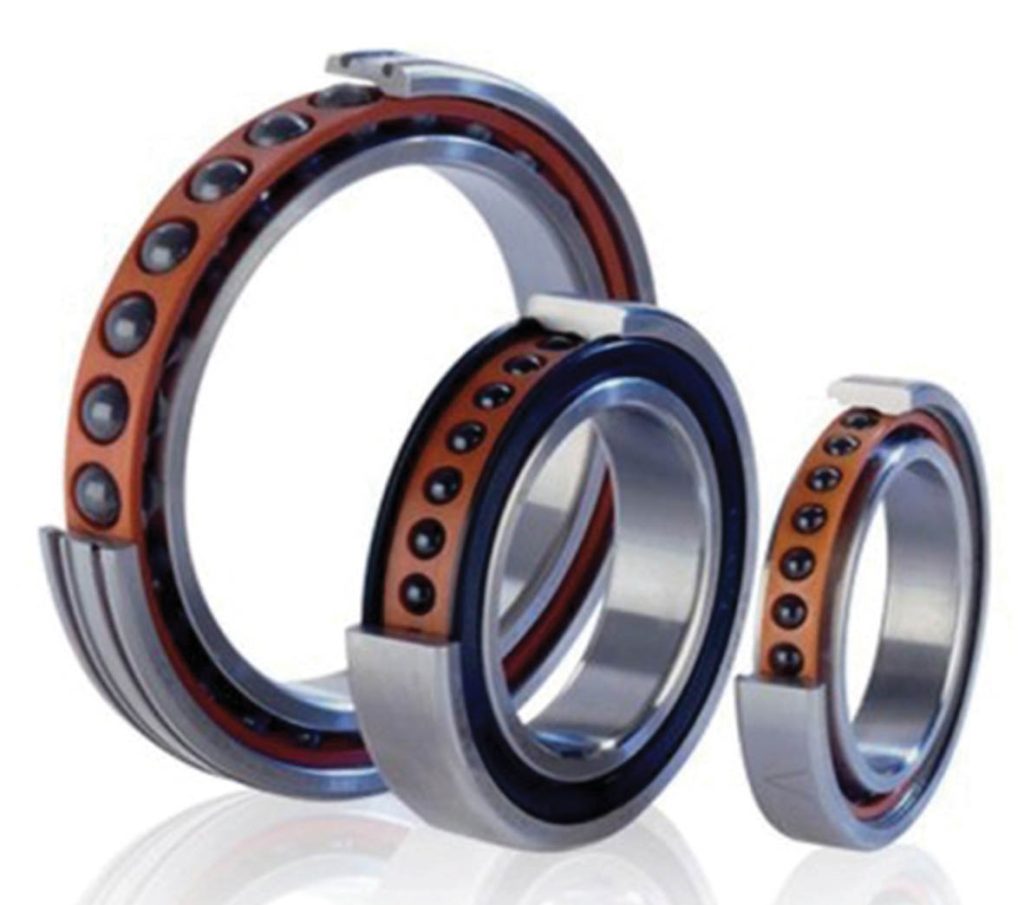

figure 2
Engine and engine oil
Some time ago, Yamaha company used ceramics to make engine cylinders in its products in a research work. This engine had very low friction and could even continue to operate without the need for a cooling system.
As a result, it had a very high efficiency, but the use of ceramics in this way was very expensive and did not bring economic justification. Metal-ceramic technology was the solution to this problem.
In this technology, the engine oil is saturated with ceramic nanoparticles and these very tiny particles fill all the microscopic depressions and elevations in the seemingly polished surface of the cylinders and bond with the walls of the cylinders under conditions of high temperature and high friction inside the cylinders.
The result of this process is the creation of a surface with 6 times less friction than a mirror and 10 times more hardness than steel. The thermal resistance and hardness of advanced ceramics have made it possible to use these materials in car and truck engines.
It is predicted that in a few years, ceramic components and metal parts with ceramic coating will be widely used in environments with very high operating temperatures, such as car engines without the need for radiators and with high fuel efficiency.
The increase in fuel efficiency of such cars is the result of lightening the car engine and also increasing the combustion temperature.
A model diesel engine with ceramic piston, cylinder and cylinder head without cooling system by “Kyocera” 1 it was made.
The experts of this company claim that the above engine works up to eight hundred thousand kilometers without the need for major repairs.
Silicon nitride, silicon carbide, alumina and zirconia are among the ceramic materials used in the internal components of engines.
Among the ceramics made with different materials that have been developed and expanded in different decades, silicon nitride and silicon carbide have attracted much attention for the construction of internal combustion engines and turbines.
These materials have a high temperature shock resistance and are very suitable for making small engines, but due to their low mechanical strength, their use is not suitable in cases where there is a limitation of bearing mechanical loads.
Another limitation of silicon nitride is that it cannot be heated to a temperature higher than 1850 degrees because it decomposes into its components (nitrogen and silicon).
In addition, ceramics made of silicon nitride are destroyed and destroyed in hot, corrosive and oxidizing environments.
Alumina is also widely used in the manufacture of electrical insulators and also in the manufacture of very small motors, but due to its high thermal conductivity and low hardness, it is not used in the manufacture of large industrial motors.
Zirconia ceramic material is also used in the construction of heat engines due to its two important features. First, this material has a high thermal capacity, and secondly, it has a low thermal conductivity.
One of the other ceramics have low thermal conductivity like this material. In other words, engines made of zirconia keep the heat produced in the combustion chamber and do not transfer it to the surrounding environment.
Therefore, the need for cooling systems has also been removed (Figure 3).
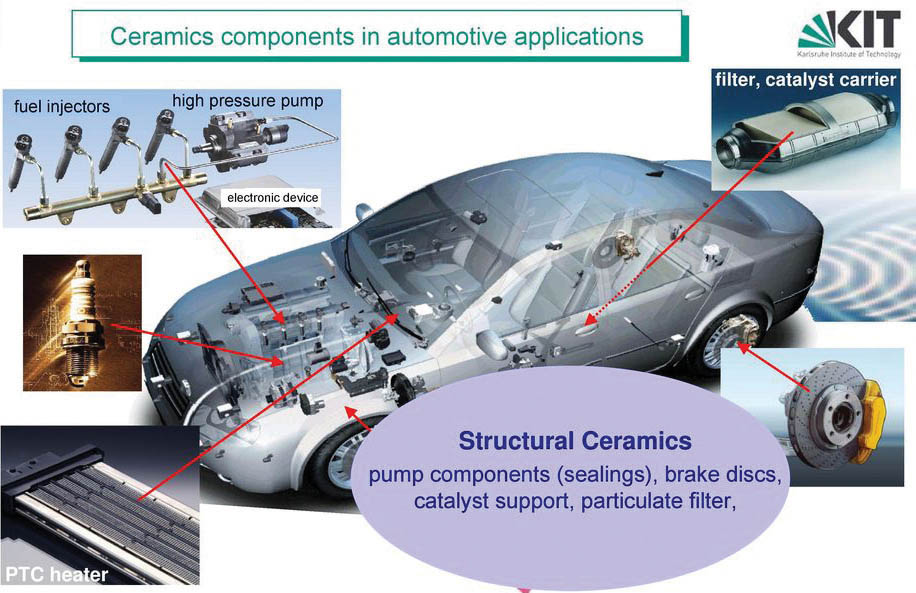
Figure 3
Brake system
As the temperature increases and the brake system heats up, the efficiency of the pads and metal discs, which are usually made of steel, suffer a severe drop.
This issue is especially important in sports and racing cars, that is, where there is a need to use the brakes continuously at high speeds.
The presence of two properties of hardness and high thermal resistance in ceramics has made these materials and their carbon composites to be considered as a suitable option for making brake pads and discs, especially in sports cars.
Because their efficiency does not decrease with increasing temperature (Figure 4).
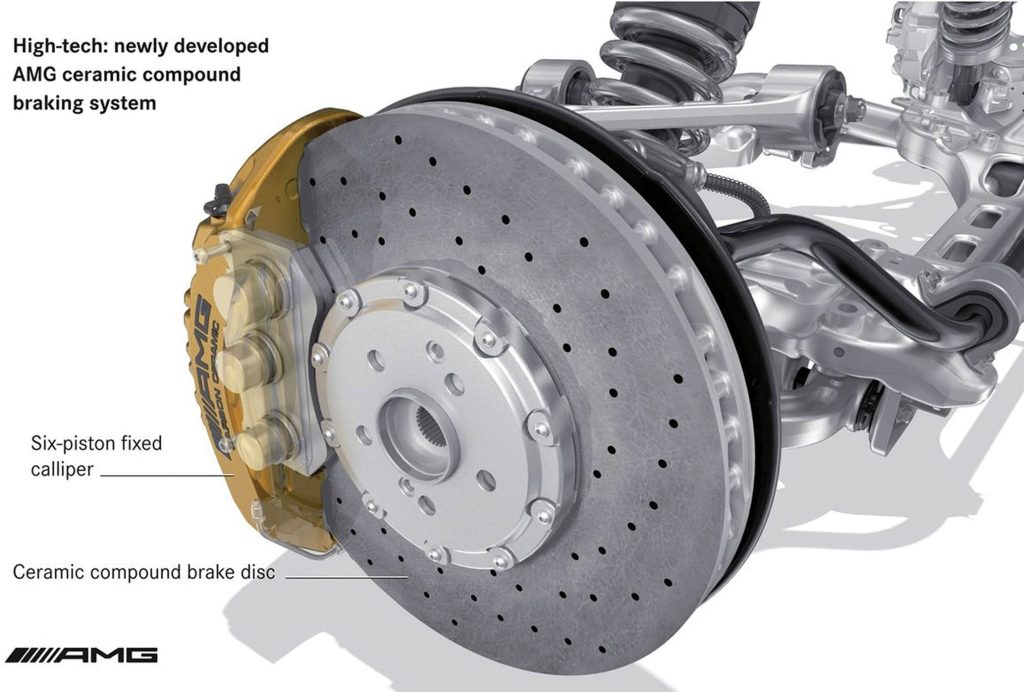
Figure 4
Battery and hybrid systems
in fact, the battery or energy source of hydrogen cars that is being designed and manufactured today is made of a type of semi-conductor ceramic that, due to its special structure and composition, is able to produce steam when it is placed in the vicinity of hydrogen. Water and electric energy act and move the car.
Types of glass and mirrors
As a large part of the family of traditional ceramics, glass has an undeniable and sometimes interesting and modern use in cars.
Various types of sunroofs and their related systems, such as the “Magic Sky” project of Mercedes-Benz and similar systems in other cars, as well as photochromic and electrochromic mirrors, depend on the unique optical and electrical properties of ceramics, which today have many applications in the automotive industry, have given.
As mentioned, there are more than 50 types of applications for ceramics in the automotive industry, some of the most important of which were mentioned.
It is predicted that by 2030, ceramic materials will be used in more than 40% of car parts, which, in addition to reducing the weight of cars, will increase the life of parts and assemblies and reduce their depreciation.
Automotive industry experts are desperately looking for solutions to reduce the cost of these materials so that they can quickly expand the use of these materials in the automotive industry (Figure 5).
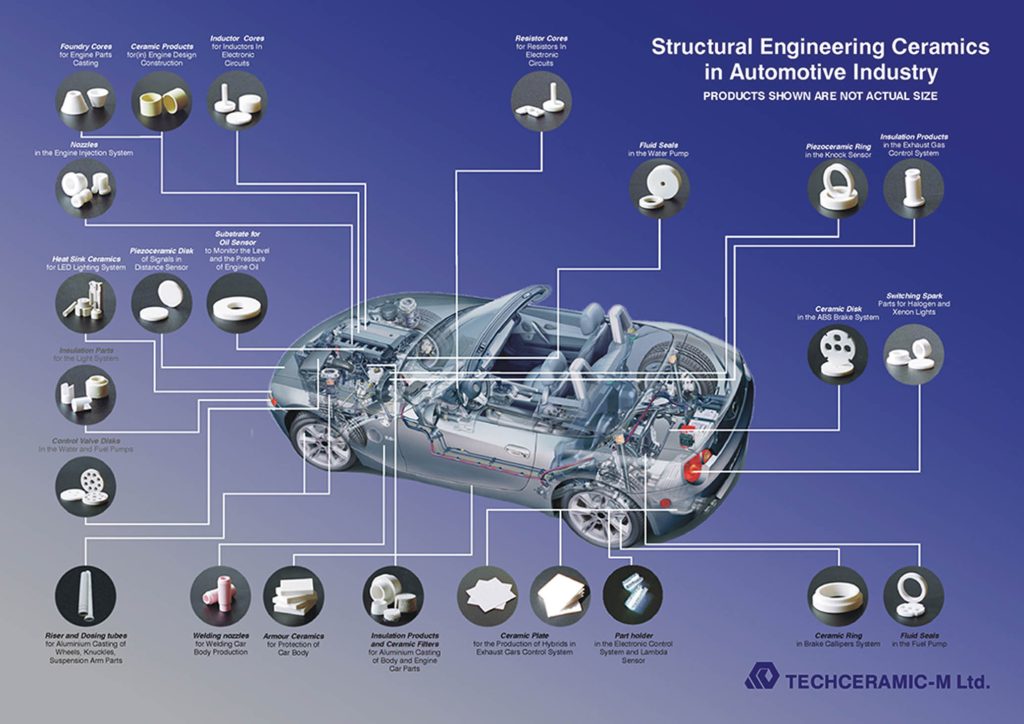
Figure 5




0 Comments