From a long time until now, engineers and car manufacturers have been in a tight competition and by using various technologies of the world, they have sought to achieve as much comfort as possible for the passengers. This was a historical milestone in the car suspension system, which we discuss in detail in this article from Act Group.
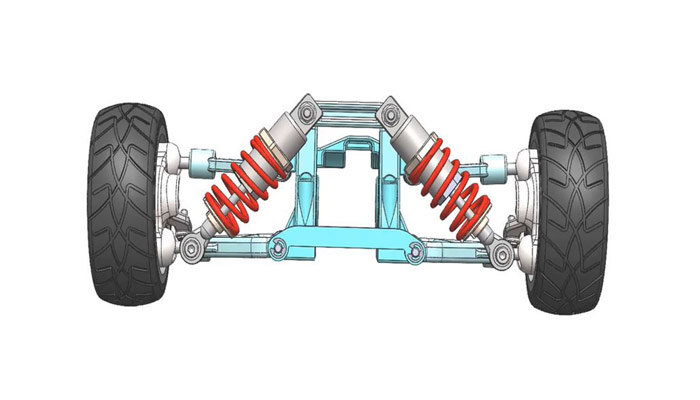
It is interesting to note that the mentioned technology did not remain in its original form and during the 7-year efforts of Mercedes-Benz engineers, by converting theoretical models into an operational plan, this company succeeded in inventing the most complex and advanced automotive technology of the last few decades called magic body control, which It uses an intelligent active suspension system and gives the passengers an amazing experience of riding on the clouds.
The effort of this research is to introduce the latest automotive technology and its engineering dimensions.
Read More : Iran Auto Parts Wholesalers
Prologue
The active body control suspension system, which was used experimentally in 2003 in the C-class model, is considered to be one of the relatively early efforts of the Benz company to improve the active suspension system of its products.
A few years later, this technology was developed and caused Mercedes to use the Peri-Scan suspension system on the F700 concept, and finally, with the advancement of equipment and computer systems, processors and sensors, after achieving the abc system, the amazing version of this family became Introduce the name magic body control to the car world.
Before dealing with this technology, it is necessary to get acquainted with the types of active-passive-semi-active suspension systems and examine the operation of each one separately in order to gain a better understanding of the active suspension system. Then we will introduce the equipment used in the mbc suspension system and we will check each individual connector.
In the following, by studying the functioning of this system, we discuss its practical working methods and technical specifications, and in the last part, by using the Matlab software as much as possible with the data and calculations of the theoretical model, we try to identify the engineering dimensions and design of a quarter model. We will have mbc technology.
Types of suspension systems in terms of engineering models
Inactive suspension system
The passive suspension system known as Passive Suspension is found in most cars today. This system consists of a number of rigid bars and connections next to the spring to absorb shocks, as well as shock absorbers to dampen shocks caused by shocks, and because this system always operates in a fixed state, regardless of the weight and condition of the vehicle, it It is called inactive.
The easiest way to introduce this system is that this type of suspension has no adjustments and changes based on the pressure applied to its various parts.
The most important drawback of these systems is that they change according to the applied pressure, and this change can have a negative effect on their operation and car handling. But instead, they are simple and have low repair and design and maintenance costs.
Self-adjusting suspension system
The most important feature of these systems is that they can keep the height of the car in a stable state based on the pressure applied to them with the help of the sensors they have. Besides, in these systems, the driver can also adjust the height of the car.
This system was initially used with the help of power and pneumatic equipment, and after the problems of these systems appeared, the adjustable suspensions moved towards the combined models of hydraulics and pneumatics, which are called hydropneumatics.
Hydropneumatic systems are more controllable, and receive and dampen shocks in a better way, which leads to an increase in the pleasure of driving a car.
Today, this system can be seen in many luxury cars of automobile companies. This suspension system is known as self leveling suspension.
Semi-active suspension system
This suspension system, which is called Semi Active Suspension, is similar to adjustable models, except that it is possible to use defaults to adjust the suspension system.
This means that the driver can choose different programmed modes of the suspension system based on his wish to adjust the stiffness and softness of the shock absorbers.
This system is available in most passenger cars in the world today, which leads to a good ride that meets the driver’s needs.
In this suspension system, hydropneumatic shock absorbers are also used, the level of activity and how they work will be controlled by a central processor.
In such cars, the activity of the suspension system changes based on the level of comfortable driving or sporty driving, and usually correspondingly, the intensity and sensitivity of the steering function also undergo changes, so that the feeling of driving is sporty or, in contrast, the feeling of a More comfortable driving, simulated and induced.
Active suspension system
In the active suspension system, the forces that enter the system from the outside are continuously checked by scanning the road surface and sensors, tensile and torsional stresses, acceleration and speed, and other parameters in real time, and based on them, in such a way that The system is adjusted so that the control and stability of the car is always in a good condition.
This means that even the mode of operation and the degree of stiffness or softness of one shock absorber among several car shock absorbers can be different from the others, so that the suspension system of the car always remains in an active state.
In this system, which is very modern and advanced, the operating force is the hydraulic force. The most obvious example of this suspension system is on the Mercedes-Benz S-Class W222, which makes the body of the car remain in a fixed line without moving up and down in any condition and while crossing any road.
Equipment used in MBC system
Stereo camera
The stereo camera, which is one of the most important components of Magic Body Control, is placed on top of the windshield and can scan the direction of the wheels up to a distance of 15 meters and with an accuracy of about 10-20 mm and when moving at a speed of 130 kilometers per hour.
Mercedes-Benz instead of using Radar systems (Distronic) or laser camera system, first introduced on the F700 concept called PRE-SCAN, placed a camera behind the mirror to scan the road surface.
A stereo camera is a 3D camera that can record images and videos in the form of a depth and detail display, so that the natural depth that the human eye can see can be seen in the image, and the elements inside it can be seen naturally in the three x, y, z axes. can be processed.
These cameras, using two or more lenses (equal to figure 1) located at a certain horizontal distance from each other, can record images in a specific format, and by sending the recorded data to the computer processor of the mbc system, the received images can be analyzed in the form of data become.

figure 1: 3D stereo camera
Sensors
Acceleration measurement in the mbc system is one of the most important parameters that is instantly analyzed by 3 accelerometer sensors in the x, y, z axes to accurately record the accelerations caused by speed and braking, as well as lateral and twisting accelerations.
This type of accelerometer is based on microelectromechanical systems (MEMS). The technology of these devices has a free end beam (cantilever beam) which is also connected to a seismic mass.
In the MBC system, the height of each wheel from the ground level should be controlled momentarily by the height sensor according to the positive and negative forces caused by the weight and movements of the vehicle, and by sending the relevant data to the processor system, it should be ready to measure the height of each wheel again after disposal. Make unevenness by variable dampers.
In the mentioned system, other sensors used in the car are jointly used, and in the above paragraphs, we examined the most important sensors of this system.
Spring help
In this section, we will introduce the types of shock absorbers that are used in semi-active and active suspension models in addition to MBC.
Pneumatic shock absorber
Pneumatic system is a type of technology that uses compressed gases to generate power. Literally, pneumatic means breath or air. This technology generally focuses on the study of compressed gases and mechanical force.
In the pneumatic shock absorber, there is a compressor in the car to send compressed air, in this case, when the piston rises in the cylinder, it faces strong resistance of the pressurized air and prevents the easy and free movement of the piston. In this type, impact force is converted into heat and using advanced dampers (equal to figure 2) can create comfort for car passengers.

figure 2: Pneumatic shock absorber
Electromagnetic shock absorber (Magneto-Rheological Fluid)
This type of shock absorber works on the basis of changing the viscosity used in it to change the oscillatory parameters. The fluid used in this shock absorber has the characteristic of viscosity depending on the magnetic field and by wrapping the metal wire around the piston rod and passing electric current through it.
The coil can create a magnetic field in the chamber and by changing the electric current, the magnetic field and as a result the viscosity of the fluid can be changed (equal to figure 3).
The electric current value of the coil is calculated by the electric control unit based on the parameters measured by the sensors and finally the variable resistance of the shock absorber is created.
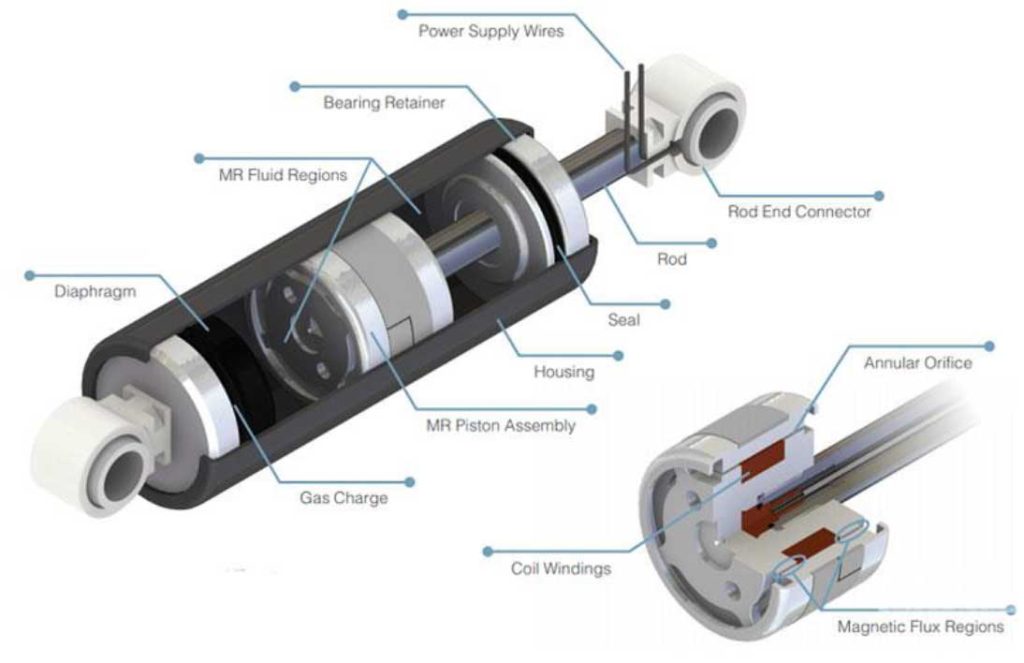
figure 3
Variable hydraulic shock absorber (Hydraulic)
In this type of advanced shock absorber that is used in smart suspension systems, unlike normal hydraulic shock absorbers that only show a repulsive reaction based on the amount of incoming force, in the system of variable hydraulic shock absorbers (figure 4-one of the variable hydraulic shock absorbers) that the mbc active suspension system is used, based on the analysis of all the sensors and cameras from the surface that the wheels come into contact with, by adjusting the oil pressure in the cylinder chamber, its stiffness is adjusted against the amount of predicted force.
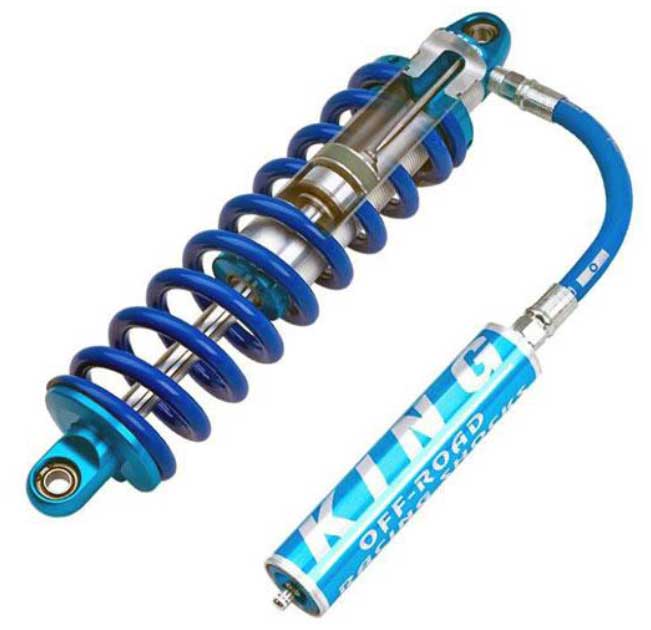

figure 4: One of the types of variable hydraulic shock absorbers
Performance
The core of the Body Control system Magic returns to complete the previous systems by means of a stereo camera sensitive to the roughness of the road surface, which is installed right in the space between the central mirror and the large windshield, and the road surface from 5 to 15 meters in front of the car with an extraordinary accuracy of 10 It scans 20 mm (equal to figure 5).
The received information about the depth, elasticity and length of the unevenness is quickly sent to the central computer of the system and then the information is sent in the form of electronic commands to the Magic Body Control system, thus the degree of softness and stiffness The suspension is adjusted before the car reaches the desired roughness.
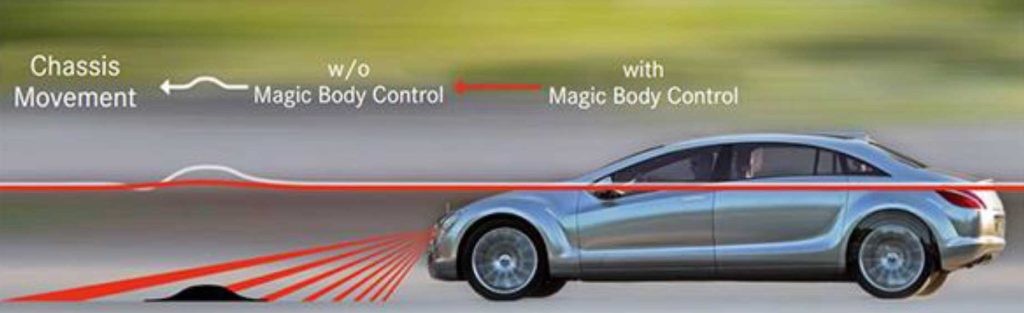
The effectiveness of this system is to the extent that it can completely neutralize the effect of a standard speed bump, so that the passengers do not feel the effect of passing such a clear unevenness.
Therefore, the distinguishing point of the suspension system of the new generation of S CLASS Compared to the previous types, it actually comes back to the same predictability, which is possible thanks to the use of a very powerful processor and the development of software for the analysis of roughness, which, of course, this issue, which may seem simple on paper, is so difficult in terms of It is a complex technique that took six years of the Mercedes-Benz chassis and suspension engineering team’s time.
The software details of how the suspension system adapts are certainly among the technical secrets of Mercedes-Benz, but the technical mechanism of the active suspension system in the new generation S CLASS has been described by the technical unit of Mercedes-Benz, which we will discuss further.
Technology
The basis of the work of adjustable suspension systems for Mercedes-Benz is to control the performance of the shock absorber or the shock absorber. Of course, there is another type of adjustable suspension that is often used for sports, tuned and racing cars that adjust the spring. In this way, the regulation is applied through a change in the host of the spring play.
However, it should be said that controlling the performance of shock absorbers is possible in several ways, which include hydropneumatic, electromagnetic or simply hydraulic type. The first type is actually a system that It was invented by Citroën and has developed significantly in recent years, although its use in some products of Rolls-Royce and Mercedes-Benz also has a history.
In the electromagnetic suspension system, suspended and very fine metal particles are used in the oil fluid flowing in the shock absorber, the oil concentration is controlled by the application of a magnetic field, and with the increase or decrease of the concentration, the reaction of the shock absorbers also changes and the suspension is drier or It becomes softer.
In more detail, how the shock absorber works depends on two factors, speed and force, a thinner fluid can move faster inside the shock absorber and less force is required to compress it, and naturally Contrary to this condition, it happens when the oil thickens in the presence of a magnetic field, which ultimately affects the working rate of the annular spring.
Finally, the system used in the latest generation of S CLASS is a combination of both types, which is largely exclusive to Mercedes-Benz. While the stereo camera monitors the quality of the road surface with extreme accuracy up to a speed of 130 km/h. , a set of 13 sensors and electric valves that are controlled by electric currents and commands from the central computer of the suspension system, are responsible for controlling the oil flow and managing the performance of the shock absorbers.
In fact, a complex set of springs and shock absorbers inside The large capsules of the suspension system are placed on each wheel, which are controlled by the flow of oil and electricity.
The remarkable point is related to the wide range of behavior of this system compared to other types of suspension systems, which, unlike many cars, is a behavior of many It offers soft and flexible to stiff and sporty, and it brings stability and stability to passengers in any situation.
In the schematic description of active suspension (equal to figure 6), it can be said that the functional structure of this technology, with the entry of x0, x1, x2 forces into the closed loop of the suspension system and the effect of certain and indeterminate masses of the car body and the reaction of the ground contact surface and the force of the loop of the suspension system, the processor By receiving all the information from the camera and sensors, the central controller analyzes the appropriate position of each wheel separately in a fraction of a second and provides the appropriate signal to the engine servo to adjust the hydraulic pressure level through the angular rotation of the hydraulic valve.
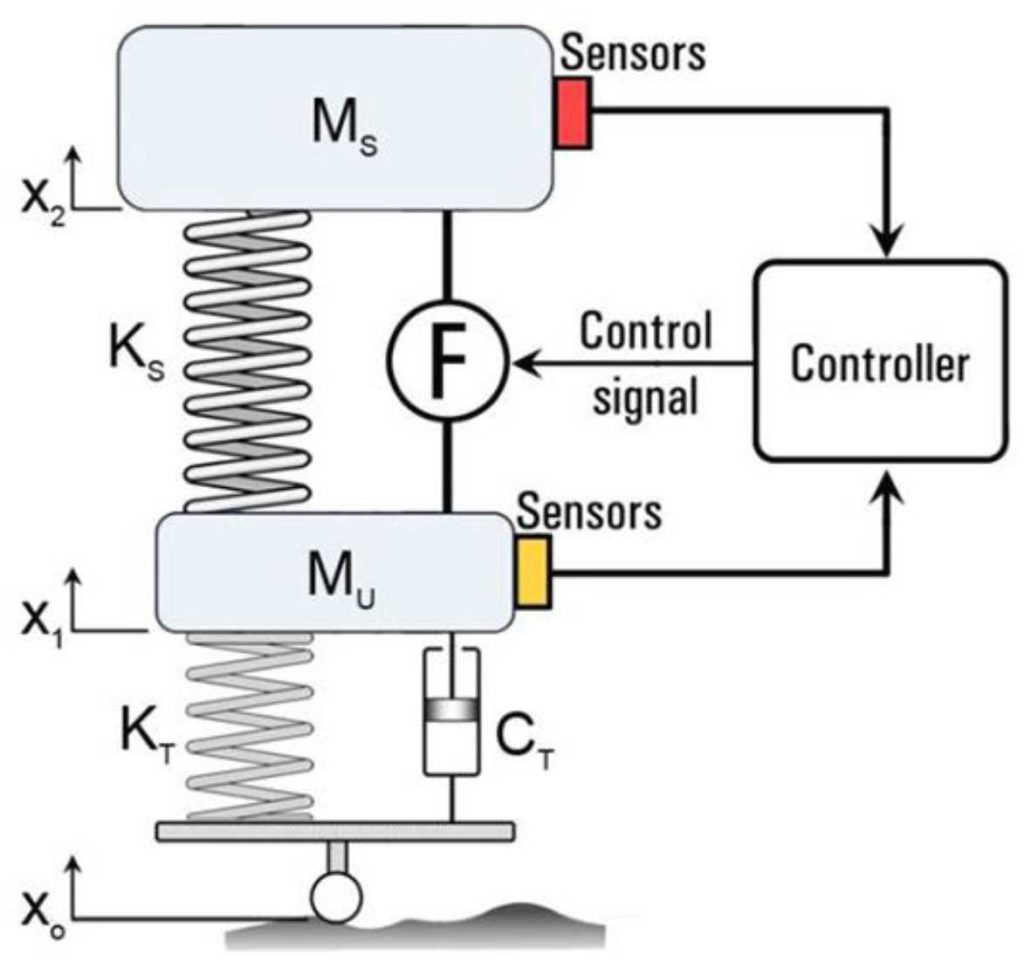
figure 6: Schematic of the functional structure of the active suspension system
In fact, in the MBC system, all four wheels are connected to each other by the flow of oil, but each wheel can also react completely independently to the unevenness, so that the overall balance of the body is stable in the best state and the passengers are the least Do not feel any effect of BODY ROLL, or disruption of stability during rapid acceleration or sudden braking.
Even as Mercedes-Benz says, the stability of the body condition is so guaranteed that the water glass inside the special S CLASS cars equipped with this system, in Going through bumps, accelerating and braking will not be overflowing.
Quality and efficiency in the long run
It was not difficult for the German engineers of Mercedes-Benz to build a complex system, but ensuring the durability of such a system in the long term is really complicated.
In 2004, a unique suspension system was invented by the famous BOSE company, which in At first, it seemed really complete and revolutionary, but long-term tests showed that this electrical system gets very hot due to continuous operation, and you can never be sure of its correct operation on a winding and uneven mountain road. Kurd, therefore BOSE’s extraordinary suspension project was put in the archive forever.
On the other hand, there have always been criticisms about the high maintenance costs of hydropneumatic suspensions like Citroen, because the hardware components of this technology require constant maintenance, and for example Many Citroën owners are struggling with problems related to periodic service issues of the not so advanced suspension system of their cars.
Mercedes-Benz engineers, as always, emphasize the high quality of their creations, and despite the high costs of production and maintenance, they will never sacrifice safety and efficiency.
Sports status
In the MBC system, in addition to the comfort mode that we talked about in detail before, another mode of this system called the sport mode is provided, and unlike the comfort mode, we see the smoothest driving and the height of the car according to the speed of movement.
It changes automatically, in sport mode, in addition to stiffer shock absorbers and drier suspension than usual, the vehicle height is also reduced by about 10 mm to create a more stable level to achieve the maneuverability of the system.
Disadvantages of excessive use of this mode include faster depreciation of system components, increased fuel consumption, and increased maintenance costs.
Meanwhile, Mercedes equipped with Magic Body Control system gives the driver the possibility to manually adjust the height of the car and the height of the car can be changed up to 30 mm.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Magic Body Control system should be mentioned as high stability in all conditions, very high riding comfort, reduction of body movements and body shakes, and reduction of the angle of the body on the sides.
And from the disadvantages of the MBC system, it can be said that due to the fact that the technical aspect of active systems cannot be implemented without measuring various parameters such as the speeds and reactions of different parts, and also since they need an external energy to activate the system, all of these cause The complexity of the components and the increase in the initial price of this system compared to the classic systems.
Although the quality and durability of Mercedes-Benz equipment is very high, the cost of maintenance and periodic services of this system is very high and sometimes destroys the economic justification for the consumer.
Also, due to the complexity of the structure and the advanced technology and equipment and the specialization of repairs, the possibility of mass production and development in other models of this company needs to correct the mentioned disadvantages.
Engineering technical dimensions and simulation model
The purpose of this part of the article is to model the car’s active suspension system using the bandgraph method and design the LQR controller for it. For this reason, the model of a quarter of the car was used to design the controller and it was applied to the full model of the car.
The model of a quarter ride of a car includes 2 degrees of freedom of movement of suspended and unsuspended mass . The model of seven degrees of freedom of driving a car includes roll, twist and yaw angles, as well as the movement of the suspension system (unsuspended masses) and suspended mass.
20-sim software has been used to model the active suspension system and MATLAB software has been used to design the controller.
Finally, by entering the data designed from the mentioned model with the help of 20-sim software and by applying the road profile, the accelerations of riding, rolling and To obtain Navoshi for two modes of active and inactive suspension system, and to extract the product graphs of matlab software through the comparative method.
Active suspension modeling
In the theoretical modeling of this article, the only difference between the active and passive suspension system is the tire and suspension system, and in this design, we will model a quarter of the suspension system (one of the tires).
Figure 7 shows the bandgraph model of the vehicle suspension system for one wheel . In this form, some differences enter the controller as a control input and the output as a force enters the suspended mass through the power source element.
Number 1 in this figure actually shows the control inputs that enter an element whose task is to take scalar numbers and provide its output in the form of a matrix. Element number 2 actually shows the K matrix, which is our optimal controller, and this matrix is obtained in the controller design part.
No. 3 includes the MSٍٍٍE element , which actually takes the controlled signal and enters the suspended mass as a force. It should be noted that the control force is a coefficient of system state variables according to the designed control. Element number 4 is also related to the movement of the suspended mass as flV speed .
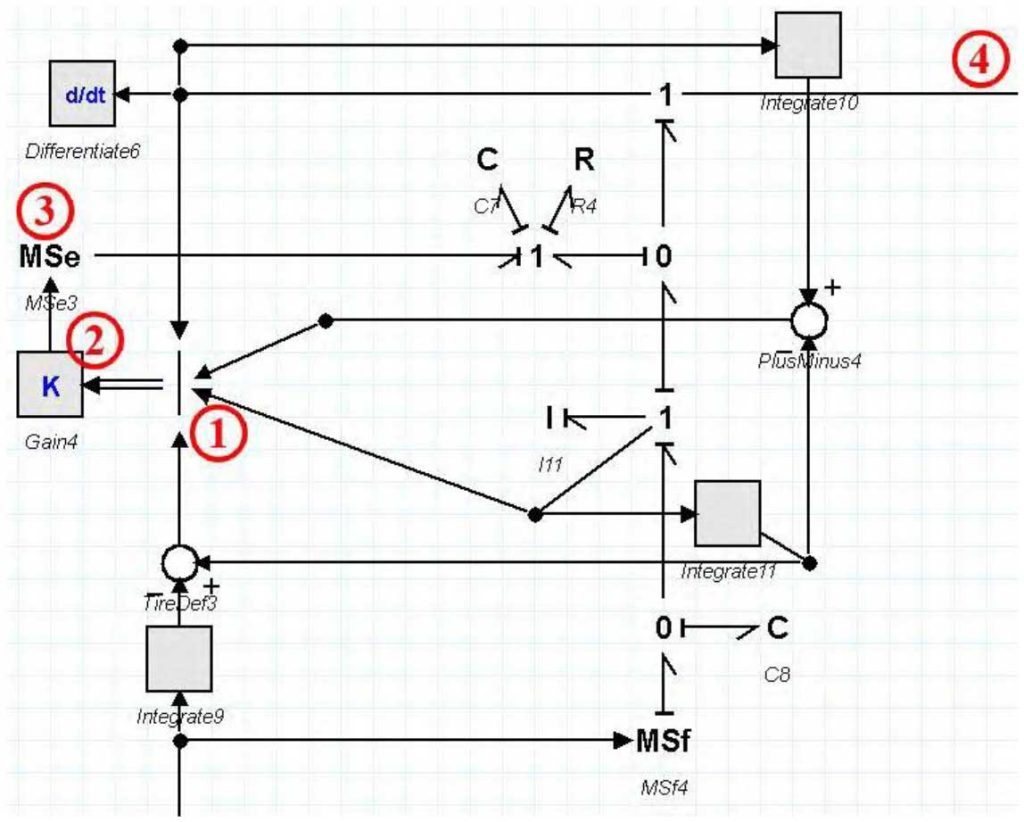
Figure 7: Bandgraph model of a quarter of active suspension
Comparative extraction graphs
As we have seen in the previous section, first the model of the active suspension system was modeled in the 20-sim software, now by using the designed controller, the values of all system elements can be obtained and they are entered into the 20-sim software, now the complete car model for Both the active suspension system and the inactive suspension system are ready for simulation.
First, we apply a road input to both systems and then we extract the accelerations related to riding movements, rolling and overturning in two time and frequency modes .
Figure 8 shows the profile of the entrance of the road that both active and passive simulation models face this roughness in order to analyze their different reactions.
Figures 9 to 11 respectively show riding acceleration, rolling acceleration and rolling acceleration in the time domain, which according to the extracted graphs, the behavior of each model is clearly comparable, figures12 to 14 show riding acceleration, rolling acceleration and rolling acceleration in the frequency domain. shows.
As it is clear from the results, the behavior of the system with the optimal controller has improved compared to the state of the system without the optimal controller.
According to figure 9, the range of vibrations of the suspended mass has decreased and the vibrations caused by the entrance of the road have been damped faster. The same thing is true for the movement of Navosh and its roll.
In order to better judge the amount of reduction in the range of vibrations, a frequency analysis has been carried out and in the figure 12 to 14 it is definitely clear that the range of oscillations has decreased especially in the sensitive frequency range for passengers ) the frequency of human body parts is between 1 and 10 and every If the fluctuation range is reduced in this part, the car has a better ride.)
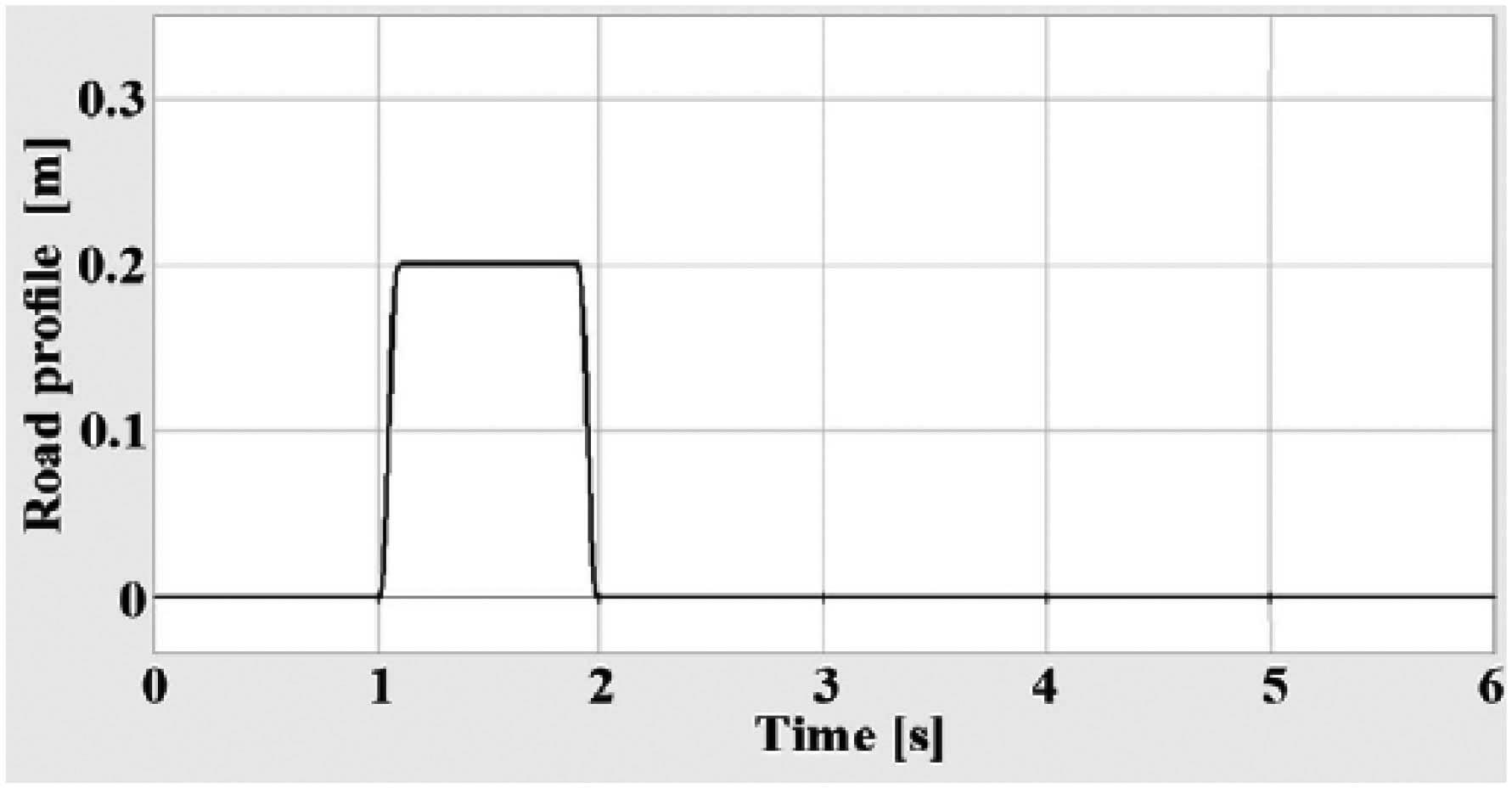
figure 8: Road entrance profile
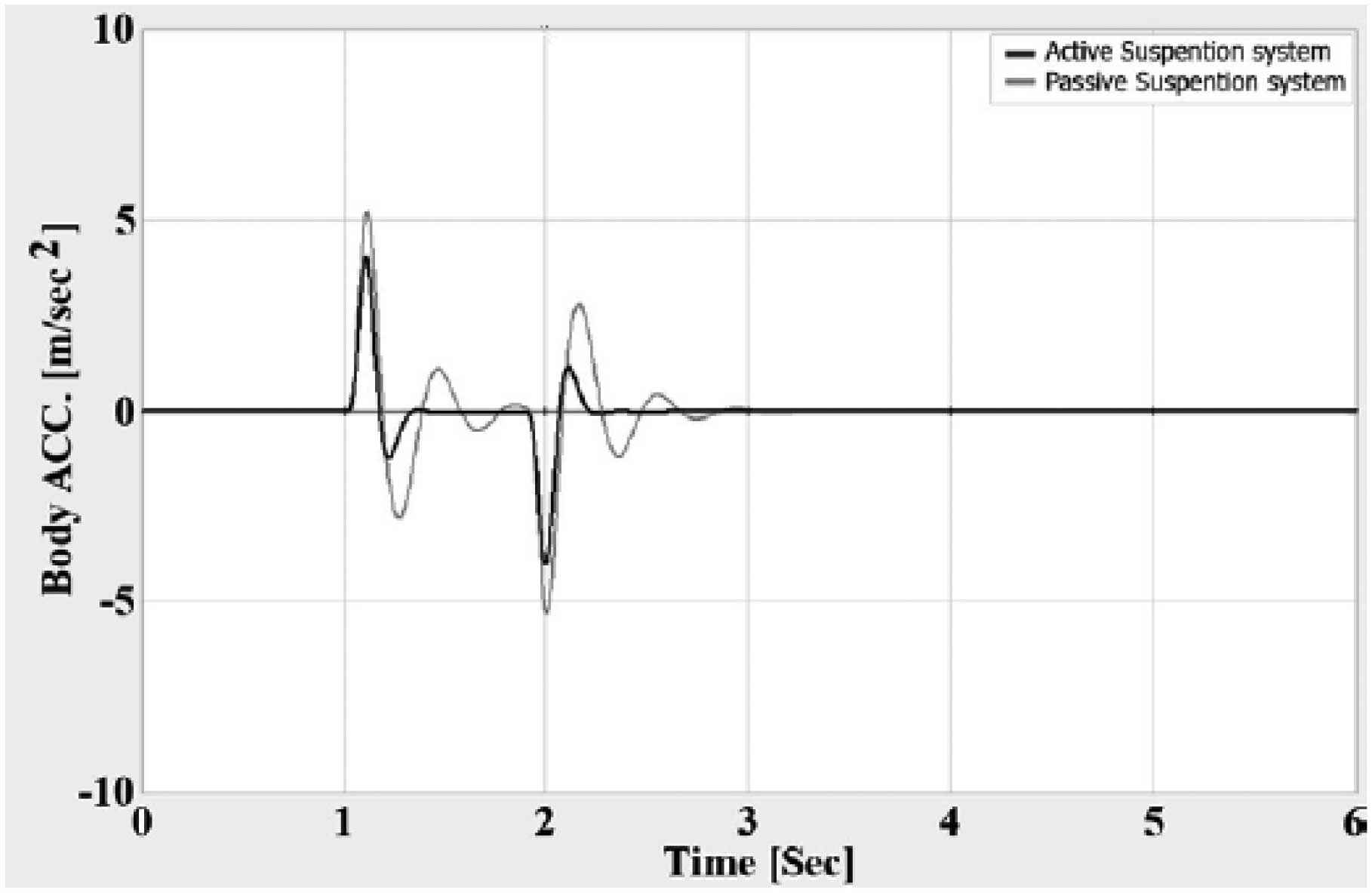
Figure 9: Acceleration graph with respect to time for two modes of active and inactive suspension system
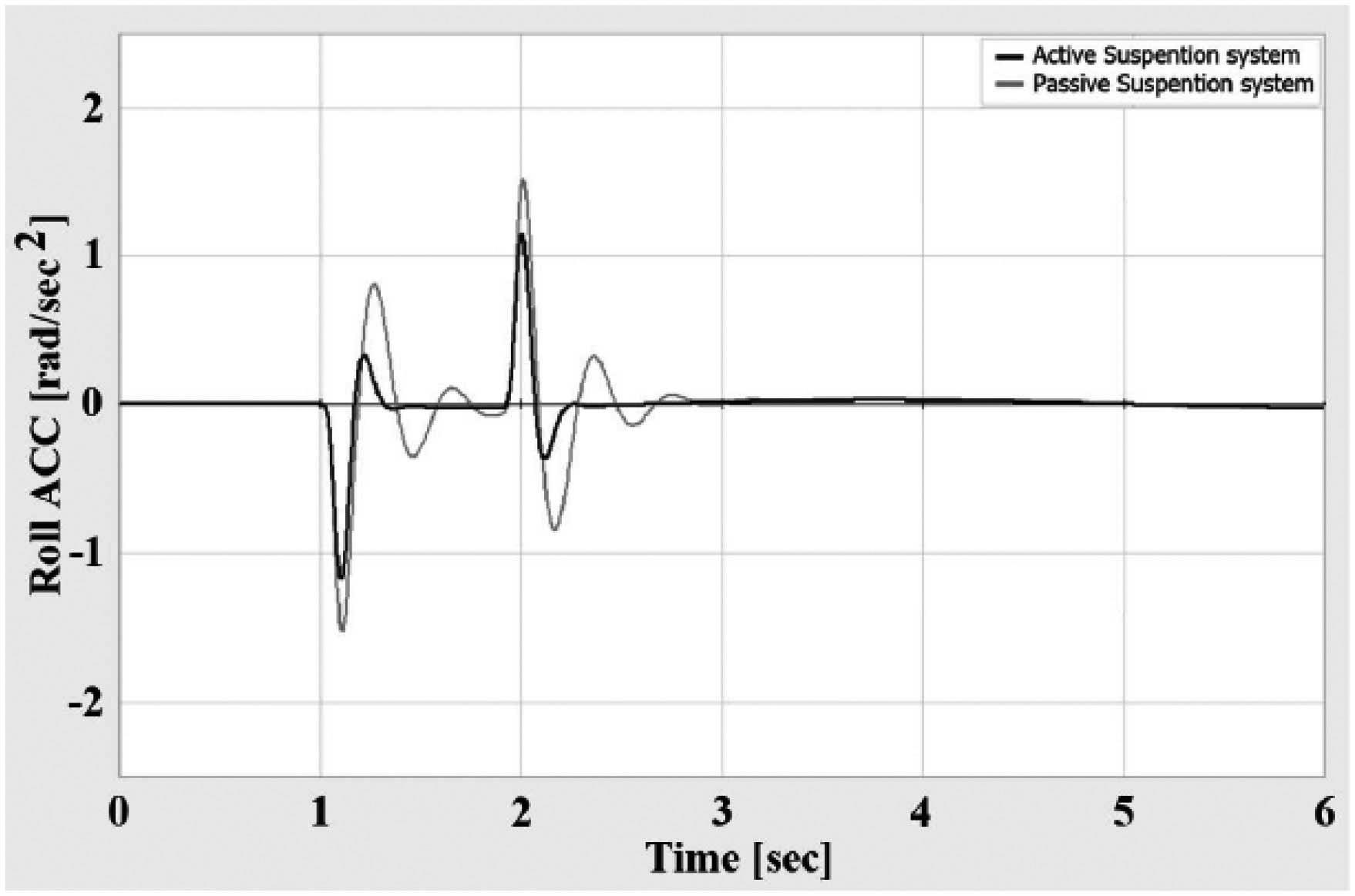
Figure 10: The graph of rolling acceleration with respect to time for two modes of active and inactive suspension system
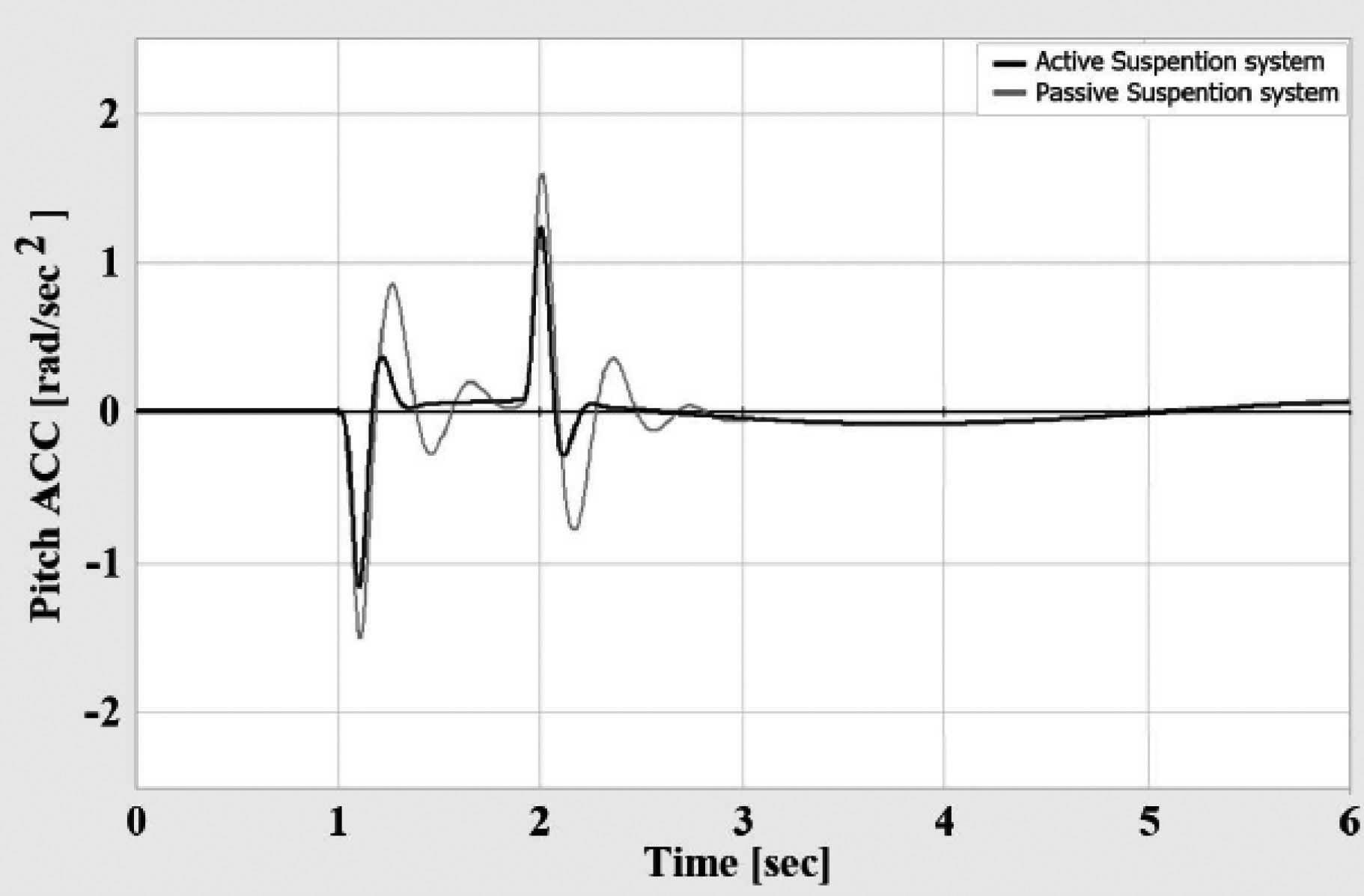
Figure 11: Naushi’s acceleration graph with respect to time for two modes of active and inactive suspension system
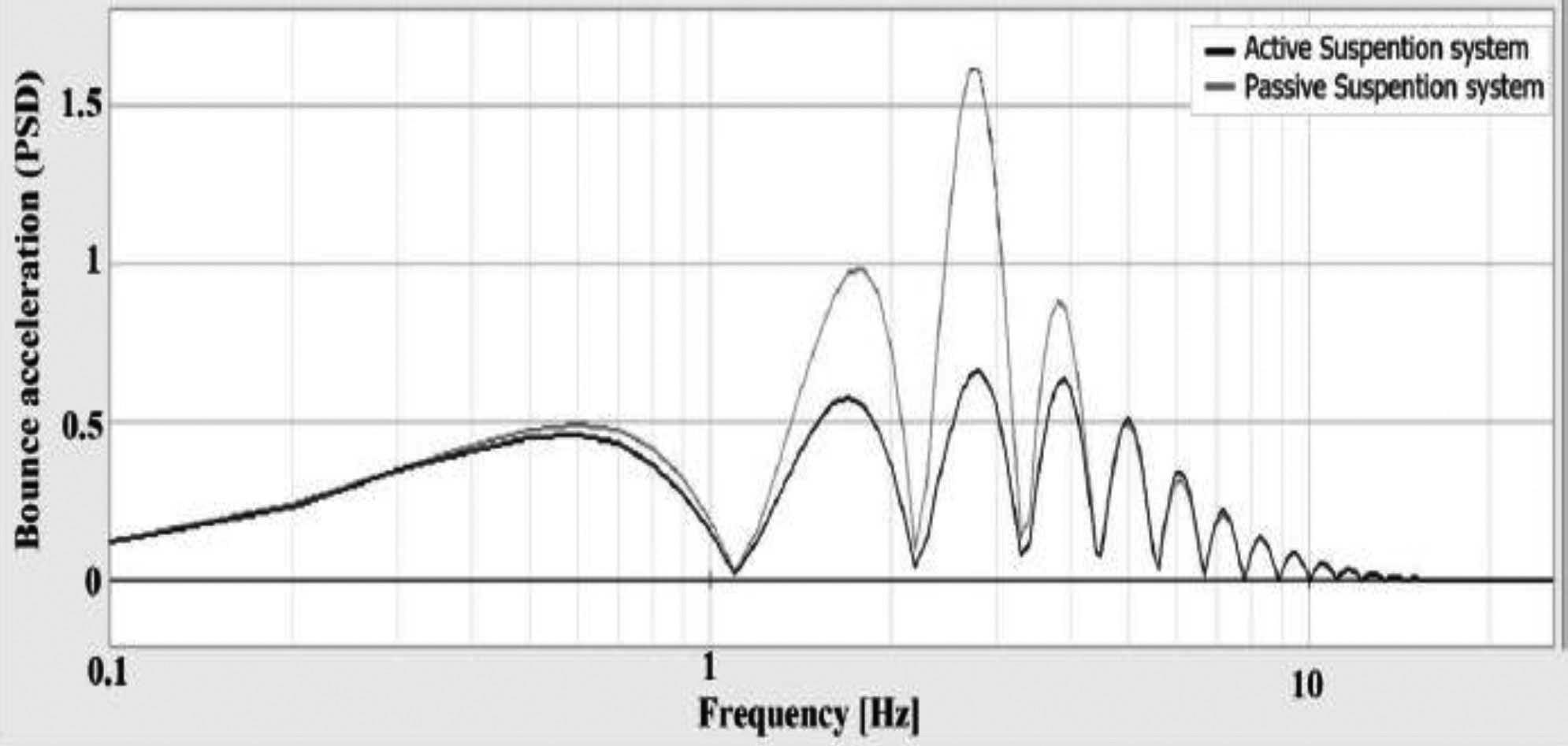
Figure 12: Acceleration chart with respect to frequency for two modes of active and inactive suspension system
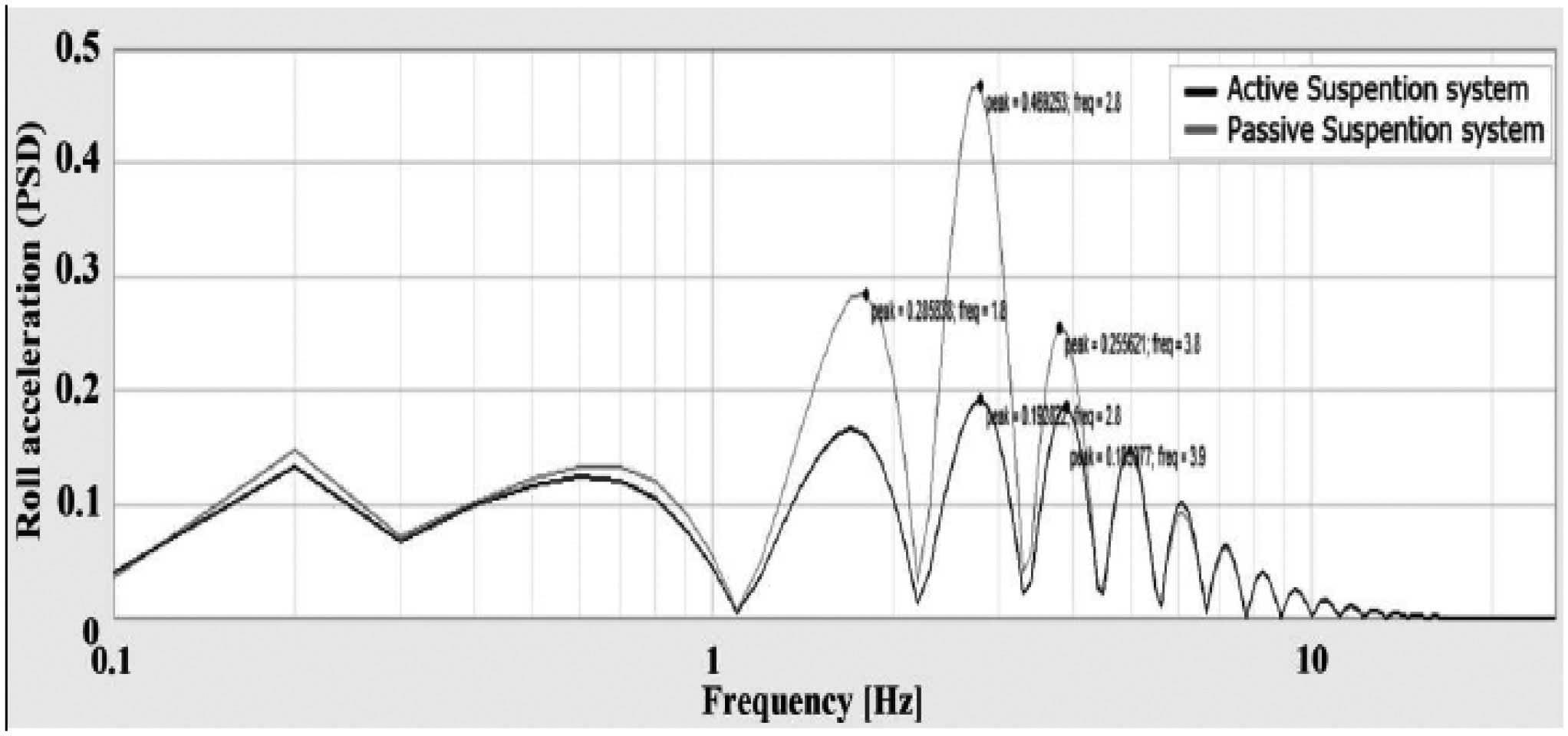
Figure 13: Graph of rolling acceleration versus frequency for two modes of active and inactive suspension system
pic
Figure 14: Naushi’s acceleration diagram with respect to frequency for two modes of active and inactive suspension system



0 Comments